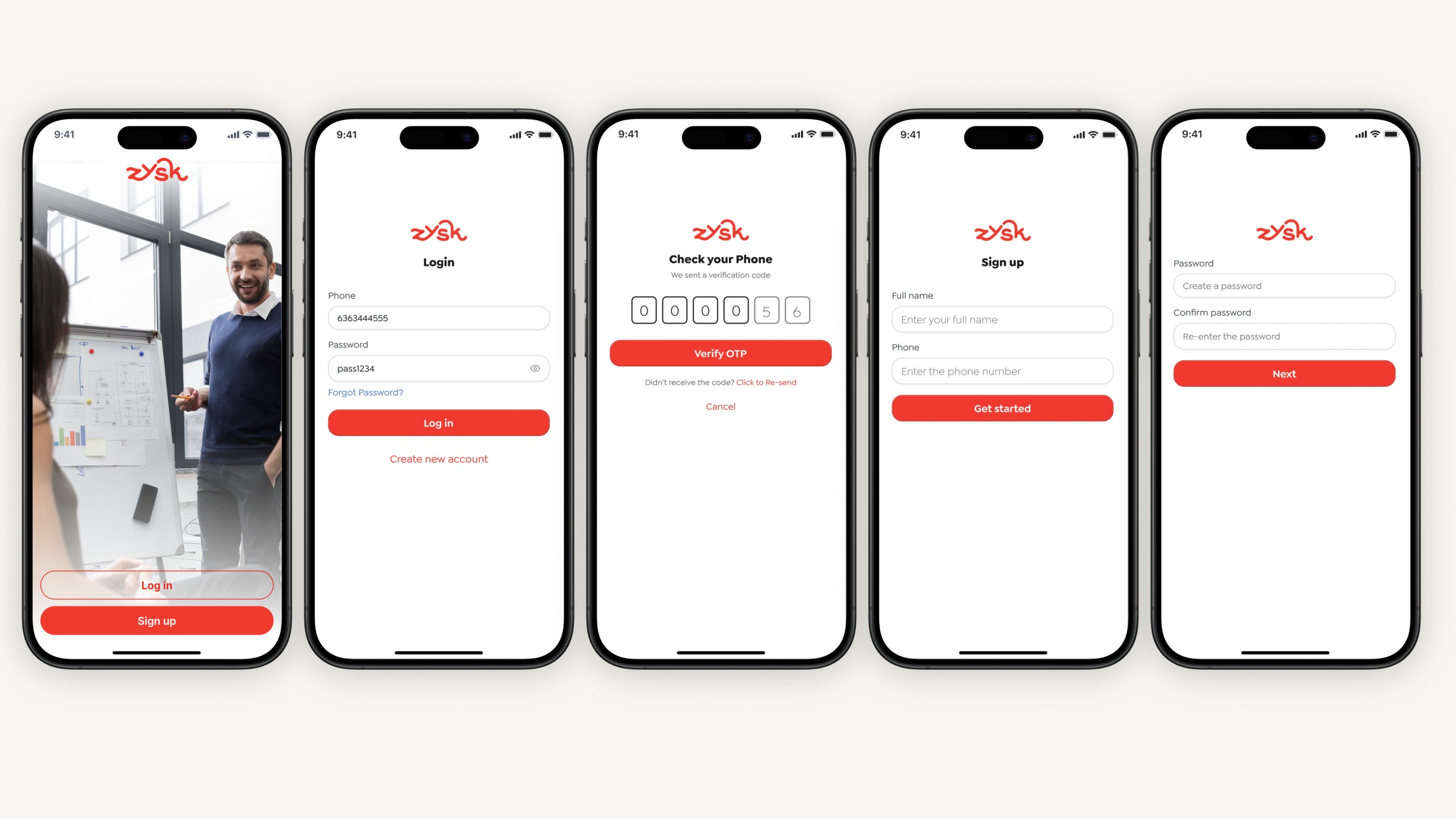
1. Clarify Your Goal and Audience
| Persona | Age | Goals | Frustrations |
|---|---|---|---|
| College Student | 20 | Track daily expenses on mobile | Complex menus, data storage caps |
| Busy Professional | 35 | Get quick budget alerts via push notifications | Slow load times, confusing UI |
| Small Business Owner | 42 | Manage invoices and payments on the go | Lack of real-time updates |
1.1 Define Your App’s Purpose
-
- Problem: What issue does your app fix?
- Solution: How does it help users on mobile devices?
- Success: Will you track installs, daily active users, or revenue?
1.2 Research Competitors Study 5–10 similar mobile apps to find gaps and ideas:
- Feature List
- Note each app’s top features and pricing model.
- User Reviews
- Read complaints to spot unmet needs.
- UI/UX Patterns
- Observe common layouts, icons, and flows.
- Cross-Industry Insights
- Look at web browser and cloud-based tools for fresh ideas.
1.3 Build User Personas Create 3–5 user profiles to guide design and development:
| Persona | Age | Goals | Frustrations |
| College Student | 20 | Track daily expenses on mobile | Complex menus, data storage caps |
| Busy Professional | 35 | Get quick budget alerts via push notifications | Slow load times, confusing UI |
| Small Business Owner | 42 | Manage invoices and payments on the go | Lack of real-time updates |
1.4 Map User Journeys Draw each persona’s path through your app:
- Discovery:How do they find your app on Google Play or the App Store?
- Onboarding:What screens guide them to set up quickly?
- Core Flow:Which tasks do they complete most often?
- Retention:What triggers (push notifications, email) bring them back?
2.Choose the Right Development Platform
2.1 Native vs. Cross-Platform vs. PWAs
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
| Native apps | Fast, direct hardware access | Two codebases (iOS app & Android) |
| Cross platform apps | Single codebase, faster build | Larger binary size, some edge cases |
| Progressive Web Apps | No app-store review, works in web browser | Limited offline, fewer device APIs |
- Native development (Swift for iOS, Kotlin for Android) excels in performance and hardware features.
- Cross-platform development (Flutter, React Native) uses one programming language and a single codebase to build both native apps.
- PWA run in any modern browser but may lack push notifications and deep device integrations.
-
- Flutter:Uses Dart, compiles to native code, offers hot-reload.
- React Native:Leverages JavaScript taps into a vast ecosystem.
3. Design for an Engaging User Experience
A smooth user interface and intuitive flow make your app stand out.
3.1 Follow Platform Conventions
- IOS apps:Use Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines for layout, typography, and gestures.
- Android apps:Follow Google’s Material Design patterns for colors, motion, and components.
Users feel at home when your interface behaves like their device’s native apps.
3.2 Wireframe and Prototype
- Wireframe
- Sketch layouts in grayscale with basic blocks.
- Prototype
- Link screens in Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD for click through demos.
- User Testing
- Run brief sessions to capture feedback on flow and design
- Wireframe
Early prototyping highlights usability issues before you start coding.
3.3 Build Responsive Layouts
- Use fluid grids and relative units (dp, pt) to adapt to all screen sizes.
- Test on a range of mobile devices, from small phones to large tablets.
- Check both portrait and landscape orientations.
3.4 Prioritize Accessibility
- Screen readers: Ensure support for VoiceOver (iOS) and TalkBack (Android).
- Text scaling: Allow users to increase font size without breaking layout.
- Color contrast: Maintain at least 4.5:1 contrast for readability.
- Touch targets: Size buttons at least 44×44 px for easy tapping.
Accessibility features not only help users with disabilities but also improve overall user experience.
4. Architect for Scale and Security
- Presentation Layer
- UI components and user interface logic.
- Domain Layer
- Business rules and use cases.
- Data Layer
- API calls, data storage, and network logic.
- Local Caching:Use Room (Android) or CoreData (iOS) for on-device data storage.
- Sync Logic:Queue local changes and push updates to your cloud-based server when the network returns.
- HTTPS/TLS: Enforce secure communication for all API requests.
- Key Storage: Store secrets in Keychain (iOS) or Keystore (Android).
- No Hard-Coding: Never embed API keys or passwords in your code.
- Analytics: Integrate Google Analytics or Mixpanel to track user behavior.
- Crash Reporting: Use Firebase Crashlytics or Sentry to capture errors and logs in real time.
5. Test Early and Often
5.1 Embrace the Testing Pyramid
| Type Test | Focus | Tools/Framework |
| Unit Tests | Individual functions and classes | JUnit, XCTest/td> |
| Integration | Module interactions | Espresso, XCTest UI |
| UI Tests | Full user scenarios | Appium, Detox |
5.2 Host Beta Programs
-
- TestFlight (iOS) and Firebase App Distribution (Android) let you share pre-release builds.
- Collect feedback on usability, speed, and stability from real users.
6. Launch, Learn, and Iterate
6.1 Optimize for App Stores
-
- Title & Keyword:Include terms like “mobile application development” and “user experience.”
- Description:Use concise, benefit-focused copy with keywords like “cross platform apps,” “native apps,” and “push notifications.”
- Visuals:Add high-quality screenshots and a short preview video.
6.2 Plan Regular Updates
- Release Cycle: Aim for monthly feature releases and security patches.
- User Feedback: Use in-app surveys and analytics to guide your road map.
- Push Notifications: Remind users of new content or features to drive re-engagement.
7.Add Advanced Features
Enhance engagement with real-time and cloud-based capabilities.
7.1 Real-Time Data and Push Notifications
- WebSockets or Firebase Realtime Database deliver instant updates.
- Configure push notifications for alerts, reminders, and promotions.
Real-time features boost retention and encourage active use.
7.2 Cloud-Based Backends
- Use AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, or Azure Functions for serverless logic.
- Store media files in S3, Firebase Storage, or Azure Blob Storage.
- Auto-scale resources to handle traffic spikes without manual intervention.
A cloud-based backend reduces infrastructure costs and simplifies scalability.
8. Manage Data Storage and Codebase
8.1 Smart Data Storage
-
- Key-Value Stores: Shared Preferences (Android), User Defaults (iOS) for small data.
- SQL Databases:Room, SQLite, or Realm for structured data.
- Cloud Sync:Firestore or REST APIs for shared data across devices.
8.2 Maintain a Single Codebase
Cross-platform development allows one codebase for both iOS and Android:
- Reuse Logic: Write UI components and business logic once.
- Faster Fixes: Apply patches in one place, deploy everywhere.
- Shared Tests: Run the same unit and integration tests across platforms.
9.Choose the Right Programming Language
The programming language you pick affects your team’s productivity and app performance.
- Swift for modern iOS app development.
- Kotlin for concise, safe Android code.
- Dart if you choose Flutter for cross platform development.
- JavaScript/TypeScript for React Native or PWAs.
Pick a language that matches your team’s skills and your chosen development platform.
10. Ensure SEO and Analytics Integration
Even mobile apps benefit from SEO and analytics best practices.
- Deep Links: Use URL schemes or App Links to open specific screens.
- Web Content: If you host a web view, optimize pages with meta tags and keywords like “user experience” and “development requires minimal setup.”
- Analytics Events: Track screen views, button taps, and conversion events to measure success.
Analytics data helps you refine features and improve user experience over time.
Conclusion
- Define your vision and audience.
- Choose the right technology.
- Design for simplicity and accessibility.
- Build secure, scalable backends.
- Test at every stage.
- Launch with strong ASO and iterate based on real data.
- Enhance your app with real-time, cloud-based features.
- Maintain a clean codebase and data strategy.